Svchost.exe is actually a system process belonging to the Microsoft Windows Operating System. It handles processes executed from DLLs. Off late, Microsoft started moving all of the functionality from internal Windows services into .dll files instead of .exe files for the sake of better re-usability. However, this created a little problem as a .dll file cannot be executed directly. Thus, the svchost.exe process was born to facilitate running those .dll files.
What I observed was, the memory hogging issue cropped up only after I turned on Automatic Updates from Microsoft. Fix this issue and make your Windows run faster.
Instructions
1. Download Windows Update v3 WindowsUpdateAgent30-x86.exe and save it to your C:\ drive.
2. Download fix_svchost.zip and extract the zip and save the file to your C:\ drive.
3. Download WindowsXP-KB927891.exe (right click and choose save as..) and save it to your C:\ drive.
4. Reboot the PC and log in to Windows in safe mode. To do this, press F8 just before the Windows logo shows up during boot and press up to choose “Safe Mode”.
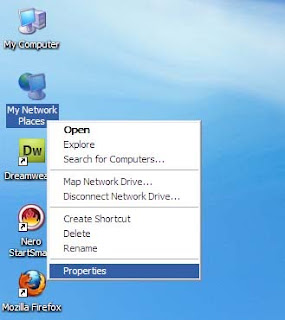
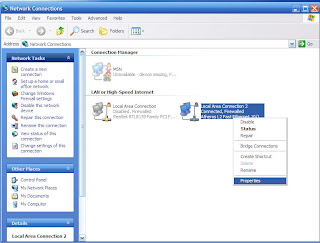
5. Login as the admin and Click Start > Run, choose the Browse button and find the fix_svchost.bat file you saved before, press Open, then OK.
6. A black screen will pop up and white text will scroll past. Wait for this process to finish as it could take several minutes. It will close itself when its finished.
7. Once the black screen disappears, Click Start > Run, choose the Browse button and find the WindowsUpdateAgent30-x86.exe file you saved before, press Open, then OK. Follow the prompts as it installs.
8. When Windows Update Agent finishes installing, Click Start > Run, choose the Browse button and find the WindowsXP-KB927891.exe file you saved before, press Open, then OK. Follow the prompts as it installs and reboot the PC.
That’s it, you are done!
DOWNLOADS INCLUDED:
1. WindowsUpdateAgent30-x86.exe
2. fix_svchost.zip
3. WindowsXP-KB927891.exe
Click Here to Download Tool
Download